Blueprints
- Consulted Sources:
- Yu, Zhouyun (1984). Palaces of the
Forbidden City. New York: Viking. ISBN
0-670-53721-7. - Oddyseey Publication's map of the
Forbidden City - Satellite images via w:Google Earth.
- Drawn by Sumple.
- Author: Sumple

Sunset of the Forbidden City, Beijing (northwest corner of the Forbidden city)
- Date: 9 June 2006
- Source: Wikipedia
- Author: User:kallgan

Hall of Preserving Harmony
- Date: February 20th, 2005
- User/Photographer: Tian Xiao Zhang
- Source: Wikipedia

Hall of Central Harmony, and Hall of Preserving Harmony
- Date: December 27, 2004
- Source: Originally posted to Flickr
- Author: Jacob Ehnmark from
Sendai, Japan - Reviewer: Eloquence

Throne in the Palace of Heavenly Purity
- Date: March 11, 2004
- Author: Yo Hibino from Lafayette IN,
United States - Reviewer: Andre Engels
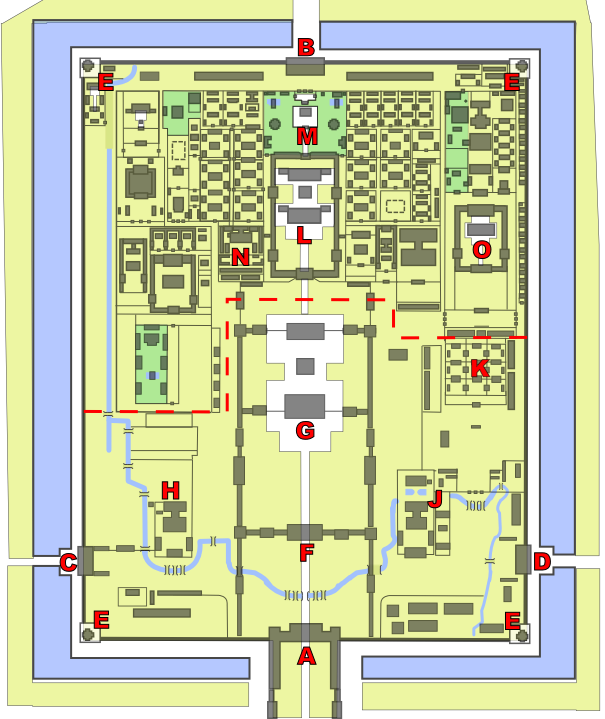
Layout
"The Forbidden City is the world's largest surviving palace complex and covers 72 ha. It is a rectangle 961 meters (3,150 ft) from north to south and 753 meters (2,470 ft) from east to west. It consists of 980 surviving buildings with 8,707 bays of rooms. The Forbidden City was designed to be the centre of the ancient, walled city of Beijing. It is enclosed in a larger, walled area called the Imperial City. The Imperial City is, in turn, enclosed by the Inner City; to its south lays the Outer City."
"The Forbidden City remains important in the civic scheme of Beijing. The central north-south axis remains the central axis of Beijing. This axis extends to the south through Tiananmen gate to Tiananmen Square, the ceremonial centre of the People's Republic of China. To the north, it extends through the Bell and Drum Towers to Yong ding men. This axis is not exactly aligned north-south, but is tilted by slightly more than two degrees. Researchers now believe that the axis was designed in the Yuan Dynasty to be aligned with Xan du, the other capital of their empire."
"The Forbidden City is surrounded by a 7.9 meters (26 ft) high city wall and a six-meter deep, 52 meters (170 ft) wide moat. The walls are 8.62 meters (28.3 ft) wide at the base, tapering to 6.66 meters (21.9 ft) at the top. These walls served as both defensive walls and retaining walls for the palace. They were constructed with a rammed earth core, and surfaced with three layers of specially baked bricks on both sides, with the interstices filled with mortar."
Wall's
"At the four corners of the wall sit towers with intricate roofs boasting 72 ridges, reproducing the Pavilion of Prince Teng and the Yellow Crane Pavilion as they appeared in Song Dynasty paintings. These towers are the most visible parts of the palace to commoners outside the walls, and much folklore is attached to them. According to one legend, artisans could not put a corner tower back together after it was dismantled for renovations in the early Qing Dynasty, and it was only rebuilt after the intervention of carpenter-immortal Lu Ban."
Gates
"The wall is pierced by a gate on each side. At the southern end is the main Meridian Gate. To the north is the Gate of Divine Might, which faces Jing shan Park. The east and west gates are called the 'East Glorious Gate' and 'West Glorious Gate'. All gates in the Forbidden City are decorated with a nine-by-nine array of golden door nails, except for the East Glorious Gate, which has only eight rows."
"The Meridian Gate has two protruding wings forming three sides of a square (Wu men, or Meridian Gate, Square) before it. The gate has five gateways. The central gateway is part of the Imperial Way, a stone flagged path that forms the central axis of the Forbidden City and the ancient city of Beijing itself, and leads all the way from the Gate of China in the south to Jing Shan in the north. Only the Emperor may walk or ride on the Imperial Way, except for the Empress on the occasion of her wedding, and successful students after the Imperial Examination."
Divisions
"Traditionally, the Forbidden City is divided into two parts. The Outer Court or Front Court includes the southern sections, and was used for ceremonial purposes. The Inner Court or Back Palace includes the northern sections, and was the residence of the Emperor and his family, and was used for day-to-day affairs of state. Generally, the Forbidden City has three vertical axes. The most important buildings are situated on the central north-south axis."
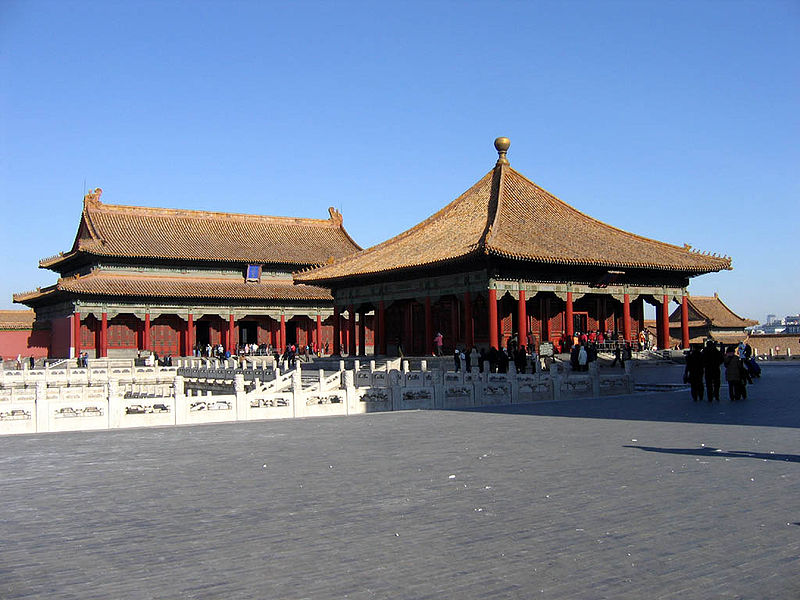
"Entering from the Meridian Gate, one encounters a large square, pierced by the meandering Inner Golden Water River, which is crossed by five bridges. Beyond the square stands the Gate of Supreme Harmony. Behind that is the Hall of Supreme Harmony Square. A three-tiered white marble terrace rises from this square. Three halls stand on top of this terrace, the focus of the palace complex. From the south, these are the Hall of Supreme Harmony, the Hall of Central Harmony, and the Hall of Preserving Harmony."
Courts
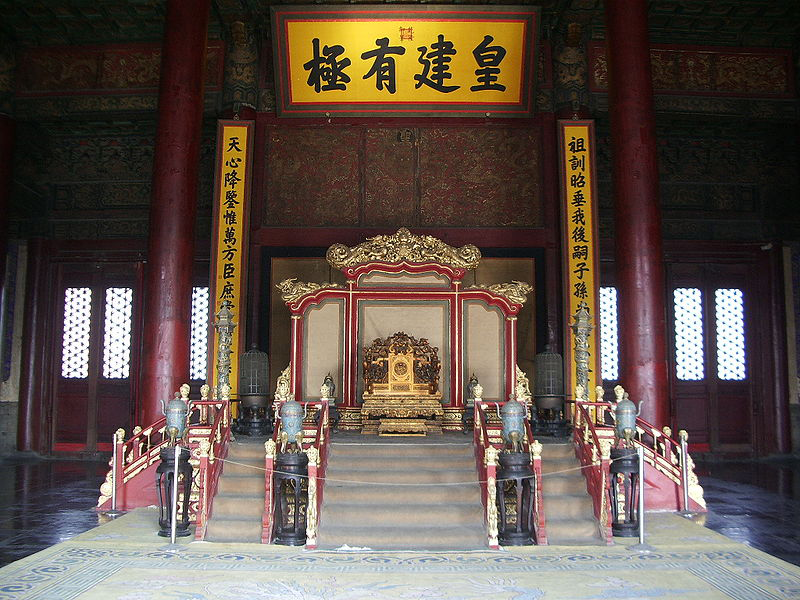
"The Hall of Supreme Harmony is the largest, and rises some 30 meters (98 ft) above the level of the surrounding square. It is the ceremonial centre of imperial power, and the largest surviving wooden structure in China. It is nine bays wide and five bays deep, the numbers 13 and 20 being symbolically connected to the majesty of the Emperor. Set into the ceiling at the centre of the hall is an intricate caisson decorated with a coiled dragon, from the mouth of which issues a chandelier-like set of metal balls, called the 'Xuan yuan Mirror'. In the Ming Dynasty, the Emperor held court here to discuss affairs of state. During the Qing Dynasty, as Emperors held court far more frequently, a less ceremonious location was used instead, and the Hall of Supreme Harmony was only used for ceremonial purposes, such as coronations, investitures, and imperial weddings."
"The Hall of Central Harmony is a smaller, square hall, used by the Emperor to prepare and rest before and during ceremonies. Behind it, the Hall of Preserving Harmony, was used for rehearsing ceremonies, and was also the site of the final stage of the Imperial examination. All three halls feature imperial thrones, the largest and most elaborate one being that in the Hall of Supreme Harmony."
Ramps
"At the centre of the ramps leading up to the terraces from the northern and southern sides are ceremonial ramps, part of the Imperial Way, featuring elaborate and symbolic bas-relief carvings. The northern ramp, behind the Hall of Preserving Harmony, is carved from a single piece of stone 16.57 meters (54.4 ft) long, 3.07 meters (10.1 ft) wide, and 1.7 meters (5.6 ft) thick. It weighs some 200 tones and is the largest such carving in China. The southern ramp, in front of the Hall of Supreme Harmony, is even longer, but is made from two stone slabs joined together - the joint was ingeniously hidden using overlapping bas-relief carvings, and was only discovered when weathering widened the gap in the 20th century."
Outwards
"In the south west and south east of the Outer Court are the halls of Military Eminence and Literary Glory. The former was used at various times for the Emperor to receive ministers and hold court, and later housed the Palace's own printing house. The latter was used for ceremonial lectures by highly regarded Confucian scholars, and later became the office of the Grand Secretariat. A copy of the Si ku Quan shu was stored there. To the north-east are the Southern Three Places, which was the residence of the Crown Prince."
Inward
"The Inner Court is separated from the Outer Court by an oblong courtyard lying orthogonal to the City's main axis. It was the home of the Emperor and his family. In the Qing Dynasty, the Emperor lived and worked almost exclusively in the Inner Court, with the Outer Court used only for ceremonial purposes."
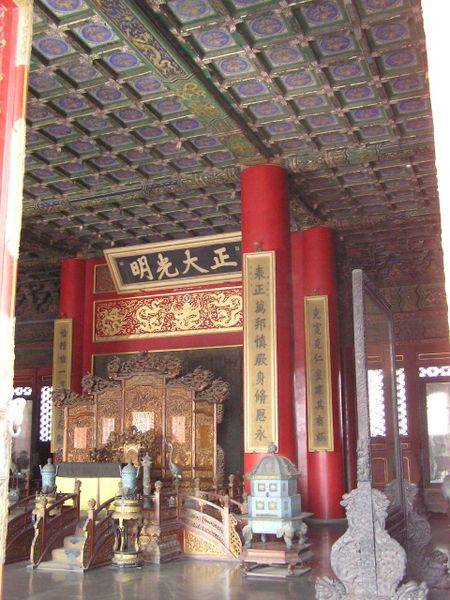
"At the centre of the Inner Court is another set of three halls. From the south, these are the Palace of Heavenly Purity, Hall of Union, and the Palace of Earthly Tranquility. Smaller than the Outer Court halls, the three halls of the Inner Court were the official residences of the Emperor and the Empress. The Emperor, representing Yang and the Heavens, would occupy the Palace of Heavenly Purity. The Empress, representing Yin and the Earth, would occupy the Palace of Earthly Tranquility. In between them was the Hall of Union, where the Yin and Yang mixed to produce harmony."
Palace's
"The Palace of Heavenly Purity is a double-leaved building, and set on a single-level white marble platform. It is connected to the Gate of Heavenly Purity to its south by a raised walkway. In the Ming Dynasty, it was the residence of the Emperor. However, beginning from the Yong zheng Emperor of the Qing Dynasty, the Emperor lived instead at the smaller Hall of Mental Cultivation to the west, out of respect to the memory of the Kang xi Emperor. The Palace of Heavenly Purity then became the Emperor's audience hall. A caisson is set into the roof, featuring a coiled dragon. Above the throne hangs a tablet reading 'Justice and Honor' (Pinyin: zhèng dà guang míng)."
"The Palace of Earthly Tranquility is a double-leaved building, 9 bays wide and 3 bays deep. In the Ming Dynasty, it was the residence of the Empress. In the Qing Dynasty, large portions of the Palace were converted for Shamanist worship by the new Manchu rulers. From the reign of the Yong zheng Emperor, the Empress moved out of the Palace. However, two rooms in the Palace of Earthly Harmony were retained for use on the Emperor's wedding night."
Gardens
"The Forbidden City is surrounded on three sides by imperial gardens. To the north is Jing shan Park, also known as Prospect Hill, an artificial hill created from the soil excavated to build the moat and from nearby lakes."
"To the west lies Zhong nan hai, a former garden centred on two connected lakes, which now serves as the central headquarters for the Communist Party of China and the State Council of the People's Republic of China. To the north-west lies Bei hai Park, also centred on a lake connected to the southern two, and a popular park."
Shrines
"To the south of the Forbidden City were two important shrines — the Imperial Shrine of Family (Pinyin: Tài miào) and the Imperial Shrine of State (Pinyin: Tài shè jì), where the Emperor would venerate the spirits of his ancestors and the spirit of the nation, respectively. Today, these are the Beijing Laboring People's Cultural Hall and Zhong shan Park (commemorating Sun Yat-sen) respectively."
Southern Gates
"To the south, two nearly identical gatehouses stand along the main axis. They are the Upright Gate (Pinyin: Duan mén) and the more famous Tiananmen Gate, which is decorated with a portrait of Mao Ze dong in the centre and two placards to the left and right: 'Long Live the People's Republic of China' and 'Long live the Great Unity of the World's Peoples'. The Tiananmen Gate connects the Forbidden City precinct with the modern, symbolic centre of the Chinese state, Tiananmen Square."
Protection
"While development is now tightly controlled in the vicinity of the Forbidden City, throughout the past century uncontrolled and sometimes politically motivated demolition and reconstruction has changed the character of the areas surrounding the Forbidden City. Since 2000, the Beijing municipal government has worked to evict governmental and military institutions occupying some historical buildings, and has established a park around the remaining parts of the Imperial City wall. In 2004, an ordinance relating to building height and planning restriction was renewed to establish the Imperial City area and the northern city area as a buffer zone for the Forbidden City. In 2005, the Imperial City and Bei hai (as an extension item to the Summer Palace) were included in the shortlist for the next World Heritage Site in Beijing."
Source: Wikipedia